Highway: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
DerpyTheNon (talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
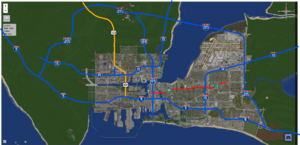
{{Infobox|image=[[File: | {{Infobox|image=[[File:Greenfield Major Roadways Map.png|thumb|Highway map as of April 11th, 2025|center]]|title=Highways in Greenfield}}There are a total of 7 highways—5 Interstate highways, 1 U.S route, and 1 state route—that exist in the city of Greenfield. All highways within the city are maintained by [[wikipedia:Caltrans|Caltrans]]. | ||
== | == History == | ||
[[File:Highway-Map.png|thumb|300px|Highway map from Update 0.5.4]] | |||
The history of Greenfield's Interstate system dates back to the 1950s when the federal government began to invest in the construction of a network of highways across the United States. The goal of this program was to improve transportation and promote economic growth by connecting cities and states across the country. In Greenfield, the construction of the Interstate system began in the late 1950s, with the construction of the first section of what would eventually become State Route 110 (SR 110). This section of the highway was designed to connect Greenfield's downtown core with the eastern suburbs. | |||
Over the next several decades, Greenfield's Interstate system continued to expand with the construction of several additional highways, including I-5, I-205, I-105, I-15, I-10, and U.S 101. These highways helped to connect Greenfield to other major cities and states in the region, such as San Francisco, Las Vegas, and its sister city Los Angeles. The construction of the Interstate system was not without its challenges, however. The building of the highways often required the acquisition of private land and the displacement of residents, which led to significant controversy and protests. Additionally, the construction of the highways led to the destruction of many historic neighborhoods and communities, which had a lasting impact on the city of Greenfield. Despite these challenges, Greenfield's Interstate system was a major success for the city, providing residents and businesses with improved economic growth. The highways also helped to promote tourism and made it easier for people to travel to and from Greenfield. | |||
However, as the years passed, the increased use of the highways also led to increased traffic congestion, making the city's traffic among the worst in the region. It also caused air and noise pollution in the city. The local government and residents have taken steps to address these issues, such as promoting public transportation and encouraging carpooling. | |||
Overall, Greenfield's Interstate system has had a significant impact on the city, both positive and negative. It has improved transportation and economic growth, but also had an impact on the environment and quality of life for residents. | |||
[[ | == Build history == | ||
The highway system will be significantly revamped in the upcoming [[Update 0.5.5]]. | |||
== List of highways == | |||
'''Interstates'''<br /> | |||
[[I-5]]<br /> | |||
[[I-10]] {{small|''(to be renamed [[SR-118]] in [[0.5.5]])''}}<br /> | |||
[[I-15]] {{small|''(to be merged into [[I-40]] in 0.5.5)''}}<br /> | |||
''[[I-40]]'' {{small|''(upcoming: 0.5.5)''}}<br /> | |||
[[I-105]] {{small|''(to be merged into [[I-40]] in [[0.5.5]])''}}<br /> | |||
[[I-205]] | [[I-205]] | ||
'''Other highways'''<br /><!-- state routes are to be delineated as "SR-x" and not "CA-x" --> | |||
''[[SR-1]]'' {{small|''(upcoming: [[0.5.5]])''}}<br /> | |||
[[SR-110]] {{small|''(to be renamed [[SR-154]] and slightly rerouted in 0.5.5)''}}<br /> | |||
[[US-101]]<br /> | |||
''[[SR-118]]'' {{small|''(upcoming: [[0.5.5]])''}}<br /> | |||
''[[SR-154]]'' {{small|''(upcoming: [[0.5.5]])''}} | |||
| | |||
}} | |||
| | |||
}} | |||
| | |||
[[Category:Transit]] | [[Category:Transit]] | ||
[[Category:Highways]] | [[Category:Highways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:48, 30 September 2025
There are a total of 7 highways—5 Interstate highways, 1 U.S route, and 1 state route—that exist in the city of Greenfield. All highways within the city are maintained by Caltrans.
History
The history of Greenfield's Interstate system dates back to the 1950s when the federal government began to invest in the construction of a network of highways across the United States. The goal of this program was to improve transportation and promote economic growth by connecting cities and states across the country. In Greenfield, the construction of the Interstate system began in the late 1950s, with the construction of the first section of what would eventually become State Route 110 (SR 110). This section of the highway was designed to connect Greenfield's downtown core with the eastern suburbs.
Over the next several decades, Greenfield's Interstate system continued to expand with the construction of several additional highways, including I-5, I-205, I-105, I-15, I-10, and U.S 101. These highways helped to connect Greenfield to other major cities and states in the region, such as San Francisco, Las Vegas, and its sister city Los Angeles. The construction of the Interstate system was not without its challenges, however. The building of the highways often required the acquisition of private land and the displacement of residents, which led to significant controversy and protests. Additionally, the construction of the highways led to the destruction of many historic neighborhoods and communities, which had a lasting impact on the city of Greenfield. Despite these challenges, Greenfield's Interstate system was a major success for the city, providing residents and businesses with improved economic growth. The highways also helped to promote tourism and made it easier for people to travel to and from Greenfield.
However, as the years passed, the increased use of the highways also led to increased traffic congestion, making the city's traffic among the worst in the region. It also caused air and noise pollution in the city. The local government and residents have taken steps to address these issues, such as promoting public transportation and encouraging carpooling.
Overall, Greenfield's Interstate system has had a significant impact on the city, both positive and negative. It has improved transportation and economic growth, but also had an impact on the environment and quality of life for residents.
Build history
The highway system will be significantly revamped in the upcoming Update 0.5.5.
List of highways
Interstates
I-5
I-10 (to be renamed SR-118 in 0.5.5)
I-15 (to be merged into I-40 in 0.5.5)
I-40 (upcoming: 0.5.5)
I-105 (to be merged into I-40 in 0.5.5)
I-205
Other highways
SR-1 (upcoming: 0.5.5)
SR-110 (to be renamed SR-154 and slightly rerouted in 0.5.5)
US-101
SR-118 (upcoming: 0.5.5)
SR-154 (upcoming: 0.5.5)